Frequently Asked Questions About BRIDION® (sugammadex)
What is the indication and usage for BRIDION?
What is the recommended dosing for BRIDION?
Dosing based on actual body weight and depth of block
Routine co-administration of an anticholinergic agent is not required.
Treatment with anticholinergic agents, such as atropine, should be administered if clinically significant bradycardia is observed.
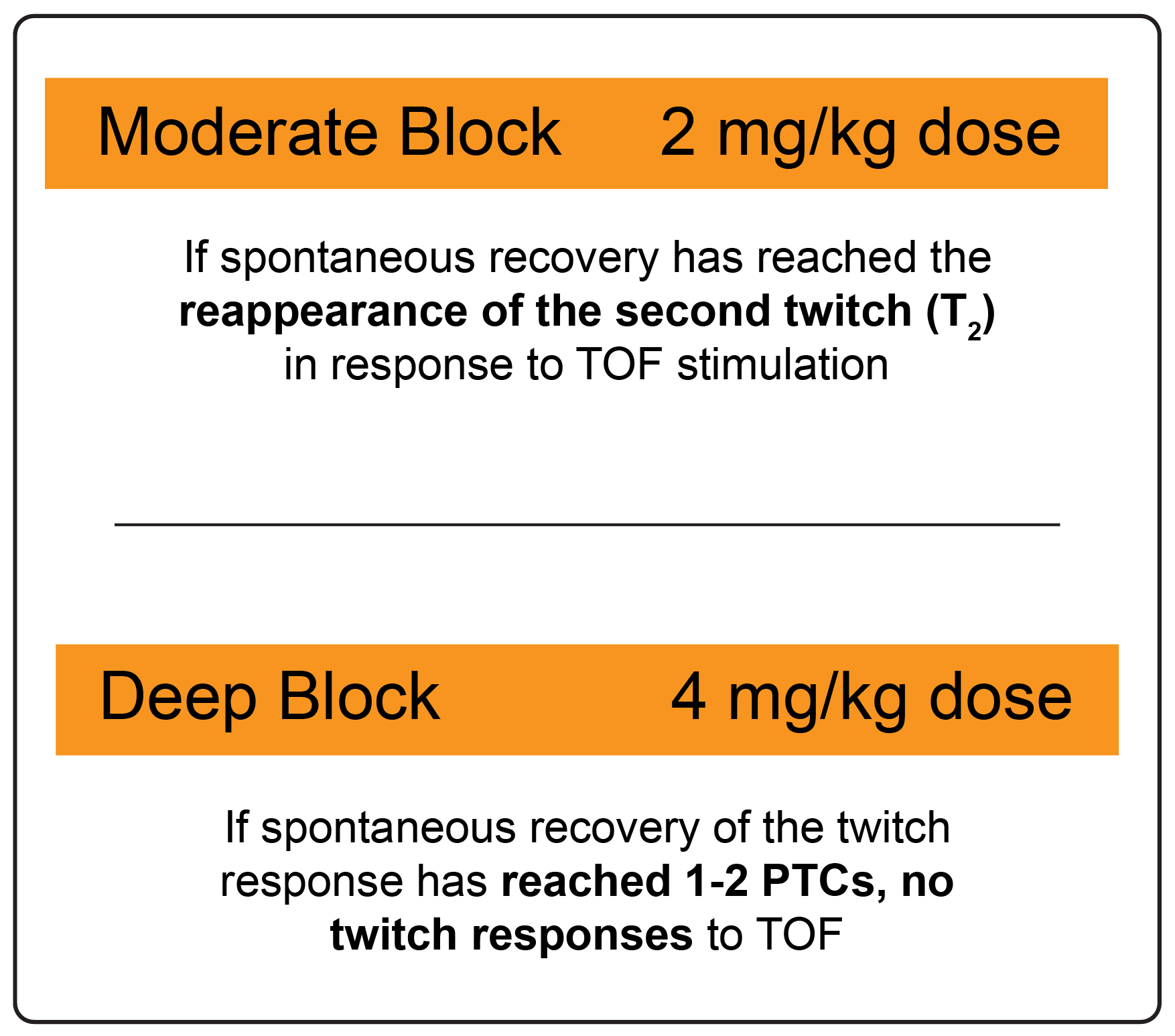
- The recommended dose of BRIDION does not depend on the anesthetic regimen.
- Administer BRIDION intravenously as a single bolus injection. The bolus injection may be given over 10 seconds into an existing intravenous line. BRIDION has only been administered as a single bolus injection in clinical trials.
- BRIDION 100 mg/mL may be diluted to a concentration of 10 mg/mL, using 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, to increase the accuracy of dosing in the pediatric population. Review the PI for additional instructions on how to dilute BRIDION for pediatric use.
No dose adjustments of BRIDION required in these special patient populations
- Geriatric patients with normal organ function
- Patients diagnosed with or who have a history of pulmonary complications
- Patients diagnosed with or who have a history of cardiac disease (eg, patients with ischemic heart disease, chronic heart failure, or arrhythmia)
- Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment
- BRIDION is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment, including those requiring dialysis.
- Obese patients with a BMI ≥40kg/m2
Drug compatibility
- May inject BRIDION into the intravenous line of a running infusion with the following intravenous solutions:
- 0.9% sodium chloride
- 5% dextrose
- 0.45% sodium chloride and 2.5% dextrose
- Ringer’s solution
- Isolyte P with 5% dextrose
- Ringer’s lactate solution
- 5% dextrose in 0.9% sodium chloride
- Ensure the infusion line is adequately flushed (eg, with 0.9% sodium chloride) between administration of BRIDION and other drugs.
- Do not mix BRIDION with other products except those listed above.
- BRIDION is physically incompatible with verapamil, ondansetron, and ranitidine.
- Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever the solution and container permit.
What is the Selected Safety Information for BRIDION?
- BRIDION is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to sugammadex or any of its components. Hypersensitivity reactions that occurred varied from isolated skin reactions to serious systemic reactions (i.e., anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock) and have occurred in patients with no prior exposure to sugammadex.
- Potentially serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred in patients treated with BRIDION. In a clinical study, anaphylaxis occurred in 0.3% (n=1/299) of healthy volunteers treated with BRIDION. The most common hypersensitivity adverse reactions reported were nausea, pruritus and urticaria and showed a dose response relationship, occurring more frequently in the 16 mg/kg group compared to the 4 mg/kg and placebo groups. Observe patients for an appropriate period of time after administration and take the necessary precautions. Anaphylaxis has also been reported in the post-marketing setting. Clinical features in anaphylaxis reports have included dermatologic symptoms; hypotension often requiring the use of vasopressors; and prolonged hospitalization and/or the use of additional respiratory support until full recovery.
- Cases of marked bradycardia, some of which have resulted in cardiac arrest, have been observed within minutes after the administration of BRIDION. Monitor for hemodynamic changes and treat with anticholinergic agents, such as atropine, if clinically significant bradycardia is observed.
- Ventilatory support is mandatory for patients until adequate spontaneous respiration is restored and the ability to maintain a patent airway is assured. Should neuromuscular blockade persist after BRIDION or recur following extubation, take appropriate steps to provide adequate ventilation.
- In clinical trials, a small number of patients experienced a delayed or minimal response to BRIDION. Monitor ventilation until recovery occurs.
- A minimum waiting time is necessary before re-administration of a steroidal neuromuscular blocking agent after administration of BRIDION.
Re-administration of Rocuronium or Vecuronium after Reversal (up to 4 mg/kg BRIDION)
| Minimum Waiting Time | NMBA and Dose to be Administered |
|---|---|
| 5 minutes | 1.2 mg/kg rocuronium |
| 4 hours | 0.6 mg/kg rocuronium or 0.1 mg/kg vecuronium |
If neuromuscular blockade is required before the recommended waiting time has elapsed, use a nonsteroidal neuromuscular blocking agent.
- Due to the administration of BRIDION, certain drugs, including hormonal contraceptives, could become less effective due to a lowering of the (free) plasma concentrations. Consider re-administration of the other drug, administration of a therapeutic equivalent drug, and/or non-pharmacological interventions as appropriate. If an oral contraceptive is taken on the same day that BRIDION is administered, the patient must use an additional, non-hormonal contraceptive method or back-up method of contraception (such as condoms and spermicides) for the next 7 days. In the case of non-oral hormonal contraceptives, the patient must use an additional, non-hormonal contraceptive method or back-up method of contraception (such as condoms and spermicides) for the next 7 days.
- Recurrence of neuromuscular blockade may occur due to displacement of rocuronium or vecuronium from BRIDION by other drugs. Mechanical ventilation may be required. Stop the administration of the drug which caused displacement, if being administered by infusion.
- The use of lower than recommended doses of BRIDION may lead to an increased risk of recurrence of neuromuscular blockade and is not recommended. Also, when drugs which potentiate neuromuscular blockade are used in the post-operative phase, recurrence of neuromuscular blockade is possible.
- BRIDION doses of up to 16 mg/kg were associated with increases in activated partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time/international normalized ratio. Carefully monitor coagulation parameters in patients with known coagulopathies; being treated with therapeutic anticoagulation; receiving thromboprophylaxis drugs other than heparin and low molecular weight heparin; or receiving thromboprophylaxis drugs and who then receive a dose of 16 mg/kg sugammadex.
- BRIDION is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment, including those requiring dialysis.
- BRIDION has not been studied for reversal following rocuronium or vecuronium administration in the ICU.
- Do not use BRIDION to reverse nonsteroidal neuromuscular blocking agents or steroidal neuromuscular blocking agents other than rocuronium or vecuronium.
- The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥ 10% of adult patients at a 2, 4, or 16 mg/kg BRIDION dose and higher than placebo rate) were vomiting (11%, 12%, or 15% versus placebo at 10%), pain (48%, 52%, or 36% versus placebo at 38%), nausea (23%, 26%, or 23% versus placebo at 23%), hypotension (4%, 5%, or 13% versus placebo at 4%), and headache (7%, 5%, or 10% versus placebo at 8%). The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥ 10% of pediatric patients 2 to <17 years of age at BRIDION doses of 2 or 4 mg/kg) were pain (65% and 61%), vomiting (14% and 13%), and nausea (10% and 11%). The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥ 10% of pediatric patients birth to < 2 years of age at BRIDION doses of 2 or 4 mg/kg) was procedural pain (40.9% and 58%).
Before administering BRIDION® (sugammadex), please read the Prescribing Information.
What is the Mechanism of Action (MOA) of BRIDION?
BRIDION works differently than neostigmine by directly encapsulating, binding, and thus inactivating rocuronium or vecuronium.1-3
After intravenous injection, BRIDION distributes through the plasma and binds to the neuromuscular blocking agents rocuronium or vecuronium to form a complex.3 BRIDION does not affect the release or breakdown of acetylcholine.2
- The reduction of free rocuronium available in the blood plasma creates a concentration gradient with the neuromuscular junction.2
- As a result, there is a shift of rocuronium into the plasma, where it is encapsulated by BRIDION.2
- This process reduces the amount of neuromuscular blocking agent available to bind to nicotinic cholinergic receptors in the neuromuscular junction, resulting in the reversal of neuromuscular blockade.
- The process is similar for vecuronium.
- The elimination half-life of BRIDION for adults with normal renal function is approximately 2 hours, with over 90% excreted within 24 hours, primarily in urine.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate and deep block for adult patients?
Following rocuronium-induced NMB, choose BRIDION® (sugammadex) to achieve rapid recovery.
aThere were 7 censored observations in the rocuronium group.
Moderate block reversal study design
Deep block reversal study design
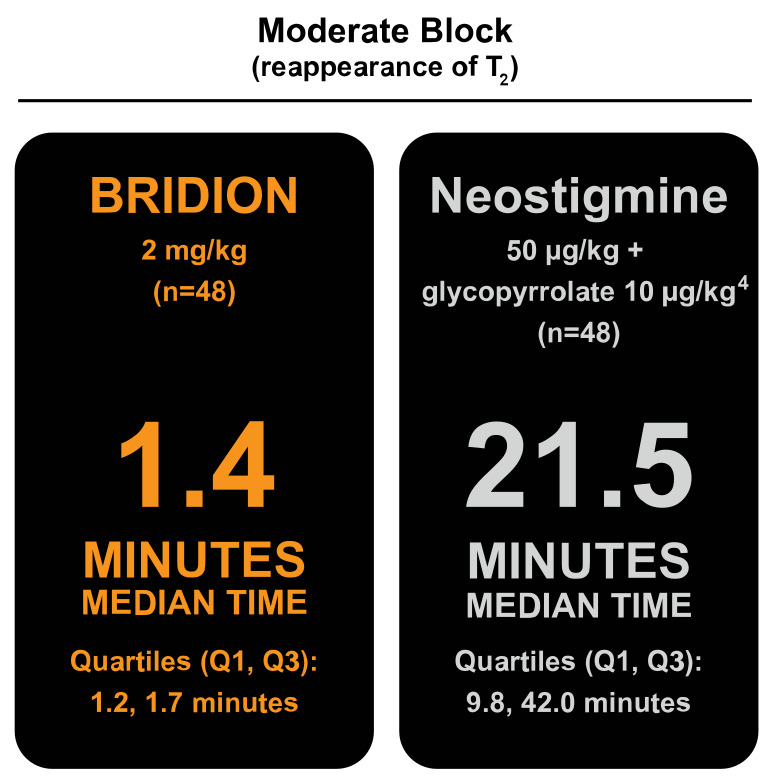
Recovery from moderate block
BRIDION® (sugammadex) achieved rapid recovery from moderate block following rocuronium- and vecuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade (NMB).
In a clinical study, BRIDION demonstrated significantly faster reversal of rocuronium-induced moderate NMB (reappearance of T2) to recovery of the train-of-four (TOF) ratio to 0.9 vs neostigmine.4
Most patients who received BRIDION recovered to a TOF ratio (T4/T1) of 0.9 within 5 minutes from the start of administration.4,5 Generally, a TOF ratio ≥0.9 correlates with recovery from NMB.
Vecuronium: Median time from vecuronium-induced moderate NMB to a TOF ratio of 0.9 was 2.1 minutes following administration of 2 mg/kg of BRIDION (Quartiles [Q1, Q3]: 1.8, 3.4 minutes; n=48) vs a median time of 29.0 minutes (Quartiles [Q1, Q3]: 12.2, 76.2 minutes; n=45) following administration of 50 μg/kg of neostigmine and 10 μg/kg of glycopyrrolate.6
Study design4,6
Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, safety-assessor-blinded study compared the efficacy of 2 mg/kg of BRIDION vs 50 μg/kg of neostigmine and 10 μg/kg of glycopyrrolate for reversal of rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced moderate NMB (reappearance of T2) in 189 patients (87 women and 102 men, ASA majority class 1, 2). Patients underwent elective procedures that were mainly endocrine; ocular; ear, nose, and throat; abdominal (gynecological, colorectal, urological); orthopedic; vascular; or dermatological in nature. An objective monitoring device (TOF-Watch® SX) was used to evaluate neuromuscular function, to measure the depth of block based on responses to TOF stimulation (TOF count or twitches), and to calculate the degree of recovery using TOF ratio (which cannot be calculated without an objective monitoring device).1,7 The primary endpoint was the time from start of BRIDION or neostigmine administration to a TOF ratio of 0.9, which generally correlates with recovery from NMB.
Recovery from deep block
BRIDION® (sugammadex) provided rapid recovery from deep block.
In a clinical study, BRIDION demonstrated rapid recovery from rocuronium-induced deep NMB (1-2 post-tetanic counts [PTCs]) to recovery of the train-of-four (TOF) ratio to 0.9.8
- The median time to recovery from deep block was similar to the moderate block study, although a wider range was observed.
- Neostigmine was not expected to reverse NMB at a depth of 1-2 PTCs.
- There were 7 censored observations in the rocuronium group.
Most patients who received BRIDION recovered to a TOF ratio (T4/T1) of 0.9 within 5 minutes from the start of administration.8 Generally, a TOF ratio ≥0.9 correlates with recovery from NMB.
Vecuronium: Median time from vecuronium-induced deep NMB to a TOF ratio of 0.9 was 3.3 minutes following administration of 4 mg/kg of BRIDION (Quartiles [Q1, Q3], 2.3, 6.6 minutes; n=47). The median time from deep block was similar to the moderate block study, although a wider range was observed. Neostigmine was not expected to reverse NMB at a depth of 1-2 PTCs. There were 6 censored observations in the vecuronium group.
Study design8,9
Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, safety-assessor-blinded study compared the efficacy of 4 mg/kg of BRIDION vs 70 μg/kg of neostigmine and 14 μg/kg of glycopyrrolate for reversal of rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced deep NMB (1-2 PTCs) in 157 patients (86 women and 71 men, American Society of Anesthesiologists class 1-3). Patients underwent elective surgical procedures that were mainly abdominal (gynecological, colorectal, urological), orthopedic, reconstructive, or neurological in nature. An objective monitoring device (TOF-Watch® SX) was used to evaluate neuromuscular function, to measure the depth of block based on responses to TOF or PTC stimulation, and to calculate the degree of recovery using TOF ratio (which cannot be calculated without an objective monitoring device).1,10 The primary endpoint was the time from start of BRIDION or neostigmine administration to recovery of a TOF ratio of 0.9, which generally correlates with recovery from NMB.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate and deep block for geriatric patients?
Recovery in geriatric patients with moderate block
In a dedicated clinical study of geriatric patients (n=102) that compared the time to recovery from rocuronium-induced moderate neuromuscular blockade (NMB), BRIDION demonstrated time to recovery of the train-of-four (TOF) ratio to 0.9 comparable with other treatment groups.11
Study design11
Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label study compared the efficacy of 2 mg/kg of BRIDION for reversal of rocuronium-induced moderate NMB (reappearance of T2) in 48 adult patients (18-64 years), 62 geriatric patients (65-74 years), and 40 older geriatric patients (≥75 years) (American Society of Anesthesiologists [ASA] class 1-3). The primary endpoint was the time from start of BRIDION administration to a TOF ratio (T4/T1) of 0.9.
Recovery in geriatric patients with deep block
In an analysis of pooled clinical trial data, BRIDION demonstrated rapid reversal of rocuronium-induced deep NMB (TOF count of 0, 1-2 post-tetanic counts [PTCs]) to recovery of the TOF ratio to 0.9 in geriatric patients.
- No dose adjustment is necessary in geriatric patients with normal organ function.
- Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate block for cardiac patients?
Study design12
Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, safety-assessor-blinded study compared the safety and efficacy of 2 mg/kg and 4 mg/kg of BRIDION for reversal of rocuronium-induced moderate NMB (reappearance of T2) in 76 patients who were diagnosed with or have a history of cardiac disease (eg, patients with ischemic disease, chronic heart failure, or arrhythmia), primarily New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class II. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the safety of BRIDION 2 mg/kg and 4 mg/kg, with the time from start of BRIDION administration to a TOF ratio of 0.9 as a secondary endpoint.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate block for pulmonary patients?
Study design13
Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, comparative, safety-assessor-blinded study compared the safety and efficacy of 2 mg/kg and 4 mg/kg of BRIDION for reversal of rocuronium-induced moderate NMB (reappearance of T2) in 77 patients who were diagnosed with or have a history of pulmonary complications (ASA class 2 and 3). The primary objective was to evaluate the safety of BRIDION 2 mg/kg and 4 mg/kg, with the time from start of BRIDION administration to a TOF ratio of 0.9 as a primary efficacy objective.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate block for obese patients?
Recovery in obesea patients
In a study of obese patients (n=188), BRIDION demonstrated statistically significantly faster recovery in patients dosed by ABW compared to IBW pooled across NMB (moderate or deep) and neuromuscular blocking agent (rocuronium or vecuronium).14
aObese is defined as a BMI ≥40 kg/m2
Study design14
Randomized, double-blind trial in 188 obese patients investigated the time to recovery from moderate or deep neuromuscular blockade (NMB) induced by rocuronium or vecuronium. Patients received 2 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg BRIDION, as appropriate for level of block, dosed according to either ABW or IBW. The primary efficacy endpoint, time to recovery of TOF ratio ≥0.9, was compared for ABW vs IBW dosing, pooled across depth of block and NMBA.
Exploratory endpoint: BRIDION and neostigmine in obese patients
The study was not designed for a comparative analysis on this exploratory endpoint and the exploratory results must be interpreted with caution.
Study design14
Randomized, double-blind trial in 188 obese patients investigated the time to recovery from moderate or deep neuromuscular blockade (NMB) induced by rocuronium or vecuronium. Patients received 2 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg BRIDION, as appropriate for level of block, dosed according to either ABW or IBW. Pooled across depth of block and neuromuscular blocking agent, the primary endpoint, ie, the median time to recover to a TOF ratio ≥0.9 in patients dosed by ABW (1.8 minutes), was statistically significantly faster compared to patients dosed by IBW (3.3 minutes). An exploratory endpoint of the study was to understand the distributions of recovery times for BRIDION and neostigmine in moderate depth of block pooled across NMBA.
What is the clinical data of BRIDION with moderate block for pediatric patients?
Recovery from rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced NMB in pediatric patients aged 2 to <17 years of age.
In a study of randomized pediatric patients 2 to <17 years of age (n=288), BRIDION (vs neostigmine) demonstrated statistically faster recovery to a TOF ratio of ≥0.9 from moderate NMB.15
These effects were consistent across age cohorts studied (2 to <6; 6 to <12; 12 to <17 years of age) and NMBA (rocuronium and vecuronium).15
Primary efficacy objective: time from start of BRIDION or neostigmine administration to recovery of a TOF ratio ≥0.9
Study design15
Time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium or vecuronium followed by administration of BRIDION or neostigmine was assessed in a randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study. The study was conducted in 288 randomized pediatric patients 2 to <17 years of age, of which 276 patients received treatment (153 boys and 123 girls; ASA class 1, 2, and 3; 89.5% were Caucasian; median weight was 25 kg; median age was 7 years). The primary efficacy objective was to evaluate the effect of BRIDION compared to neostigmine for reversal of moderate neuromuscular blockade as measured by time to recovery to a TOF ratio of ≥0.9.
Recovery from rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced NMB in pediatric patients from birth to <2 years old.
In a study of randomized pediatric patients from birth to <2 years of age (n=145), BRIDION (vs neostigmine) demonstrated statistically faster recovery from moderate NMB.
These effects were consistent across age cohorts studied (birth to 27 days, 28 days to <3 months, 3 months to <6 months, 6 months to <2 years of age).
Primary efficacy objective: time from start of BRIDION or neostigmine administration to recovery from moderate NMB
Study design
Time to recovery from neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium or vecuronium followed by administration of BRIDION or neostigmine was assessed in a randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study. The study was conducted in 145 randomized pediatric patients from birth to <2 years of age, of which 138 patients received treatment (92 boys and 46 girls; ASA class 1, 2, and 3; 68% were White; median weight was 5.8 kg; median age was 100.5 days). The primary efficacy objective was to evaluate the time to neuromuscular recovery of BRIDION in comparison to neostigmine for the reversal of moderate neuromuscular blockade.
Abbreviations
- ABW = actual body weight
- ASA = American Society of Anesthesiologists
- BMI = body mass index
- CI = confidence interval
- IBW = ideal body weight
- NMB = neuromuscular blockade
- NMBA = neuromuscular blocking agent
- NYHA = New York Heart Association
- PI = prescribing information
- PTC = post-tetanic count
- TOF = train-of-four
- T2 = second twitch
References
- Claudius C, Fuchs-Buder T. Neuromuscular monitoring. In: Gropper MA, ed. Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2020:1354-1372.
- Bom A, Hope F, Rutherford S, et al. Preclinical pharmacology of sugammadex. J Crit Care. 2009;24(1):29-35.
- Gijsenbergh F, Ramael S, Houwing N, et al. First human exposure of Org 25969, a novel agent to reverse the action of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesiology. 2005;103(4):695-703.
- Blobner M, Eriksson LI, Scholz J, et al. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade with sugammadex compared with neostigmine during sevoflurane anaesthesia: results of a randomised, controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010;27(10):874-881.
- Data available on request from Merck & Co., Inc., Professional Services-DAP, WP1-27, PO Box 4, West Point, PA 19486-0004. Please specify information package US-XBR-02067.
- Khuenl-Brady KS, Wattwil M, Vanacker BF, et al. Sugammadex provides faster reversal of vecuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade compared with neostigmine: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(1):64-73.
- Data available on request from Merck & Co., Inc., Professional Services-DAP, WP1-27, PO Box 4, West Point, PA 19486-0004. Please specify information package US-XBR-02069.
- Jones RK, Caldwell JE, Brull SJ, et al. Reversal of profound rocuronium-induced blockade with sugammadex: a randomized comparison with neostigmine. Anesthesiology. 2008:109(5):816-824.
- Lemmens HJ, El-Orbany Ml, Berry J, et al. Reversal of profound vecuronium-induced neuromuscular block under sevoflurane anesthesia: sugammadex versus neostigmine. BMC Anesthesiol. 2010;10:15.
- Data available on request from Merck & Co., Inc., Professional Services-DAP, WP1-27, PO Box 4, West Point, PA 19486-0004. Please specify information package US-XBR-02068.
- McDonagh DL, Benedict PE, Kovac AL, et al. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of sugammadex for the reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in elderly patients. Anesthesiology. 2011;114(2):318-329.
- Dahl V, Pendeville PE, Hollmann MW, et al. Safety and efficacy of sugammadex for the reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in cardiac patients undergoing noncardiac surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009;26(10):874-884.
- Amao R, Zornow MH, Cowan RM, et al. Use of sugammadex in patients with a history of pulmonary disease. J Clin Anesth. 2012;24(4):289-297.
- Horrow JC, Li W, Blobner M, et al. Actual versus ideal body weight dosing of sugammadex in morbidly obese patients offers faster reversal of rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced deep or moderate neuromuscular block: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021;21(1):62.
- Voss T, Wang A, DeAngelis M, et al. Sugammadex for reversal of neuromuscular blockade in pediatric patients: Results from a phase IV randomized study. Pediatric Anesthesia. 2022;32:436-445. DOI: 10.1111/pan.14370
