Primary endpoint: 6-minute walk distance (6MWD)
In STELLAR, a 24-week study of adults with PAH on background therapy:
WINREVAIR delivered a significant step forward for patients

Actor Portrayal
Patients taking WINREVAIR walked
41 meters moreᵃ (95% CI: 28: 54; P<0.001)
in 6 minutes at 24 weeks than patients on background therapy alone
Placebo-adjusted median increase from baseline in 6MWD
In a 24-week clinical study of adults with PAH (WHO Group 1, FC II or III) on stable background therapy, patients (N=323) were randomized 1:1 to WINREVAIR (n=163) or placebo (n=160) administered by subcutaneous injection once every 3 weeks.1
Change from baseline in 6MWD at week 24 in subgroupsa,b

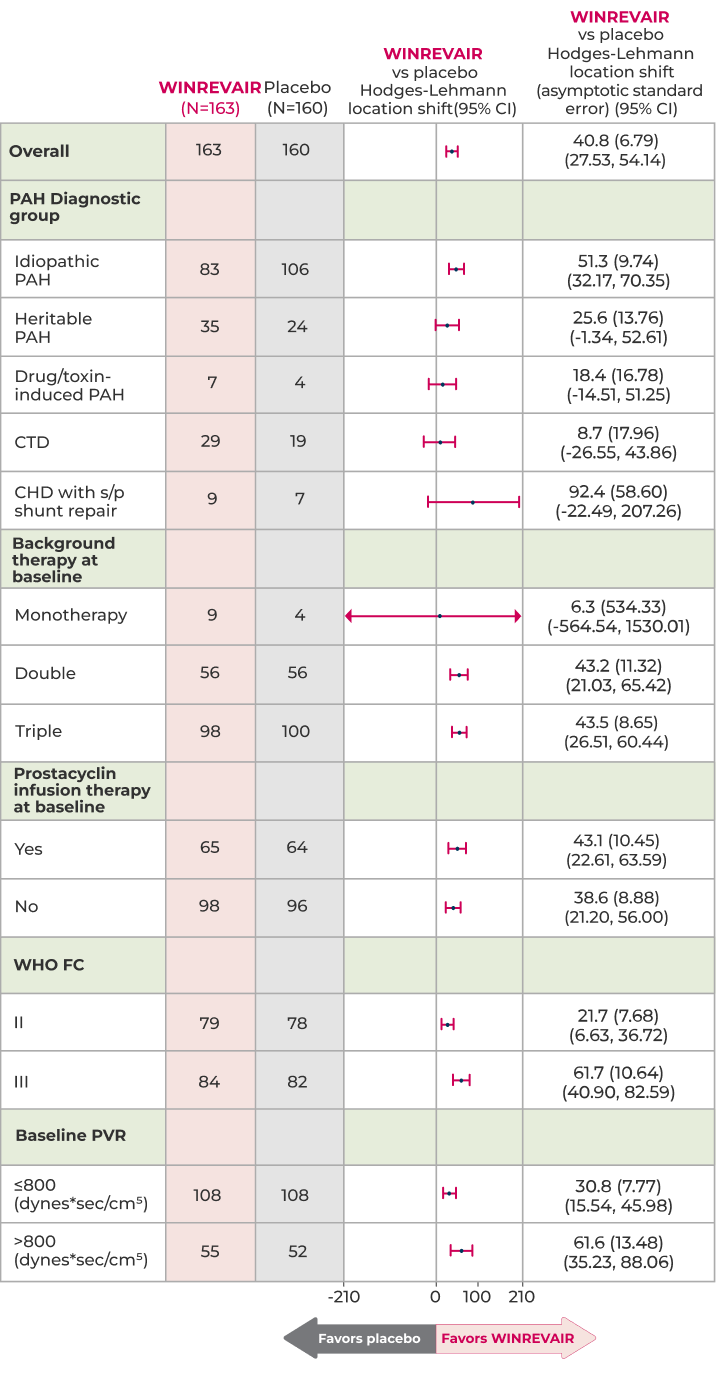

Positive improvement trends were observed in prespecified subgroups, including double and triple therapy, and WHO FC II and III
These subgroup data were consistent with the primary endpoint
ᵃHodges-Lehmann location shift from placebo estimate (median of all paired differences).
ᵇChange from baseline in 6MWD at week 24 for subjects who died was imputed to -2000 meters to receive the worst rank. Change from baseline in 6MWD at week 24 for subjects who had missing data due to a non-fatal clinical worsening event was imputed to -1,000 meters to receive the next-worst rank.
CHD = congenital heart disease; CI = confidence interval; CTD = connective tissue diseases; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance; s/p = systemic-to-pulmonary.
Reference:
1. Hoeper MM, Badesch DB, Ghofrani HA, et al; STELLAR Trial Investigators. Phase 3 trial of sotatercept for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(16):1478-1490.
