Selected secondary endpoints
In STELLAR, a 24-week study of adults with PAH on background therapy:
MORE than 2x as many patients taking WINREVAIR improved by at least 1 WHO FC
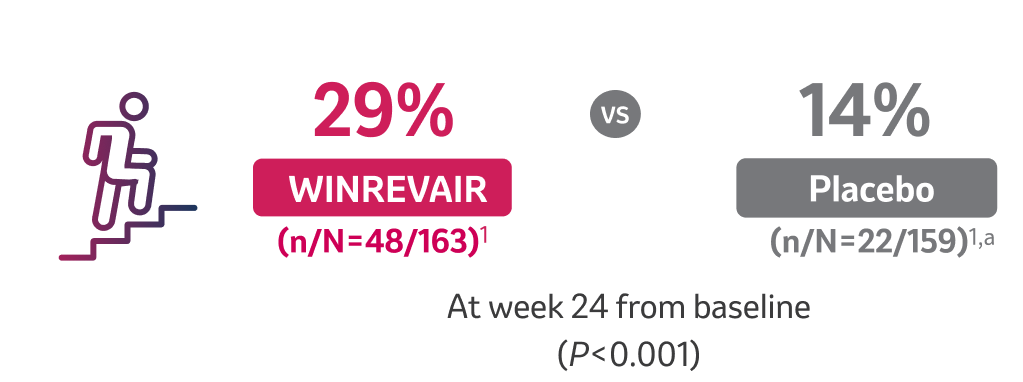
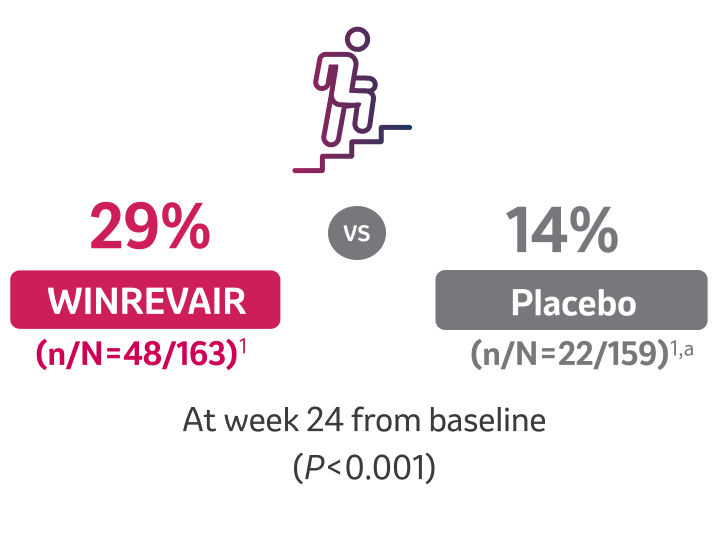
aOne patient in the group had missing data owing to COVID-19 and was excluded from the analysis.1
MORE time—WINREVAIR substantially reduced the occurrence of death from any cause or PAH clinical worsening events vs placebo
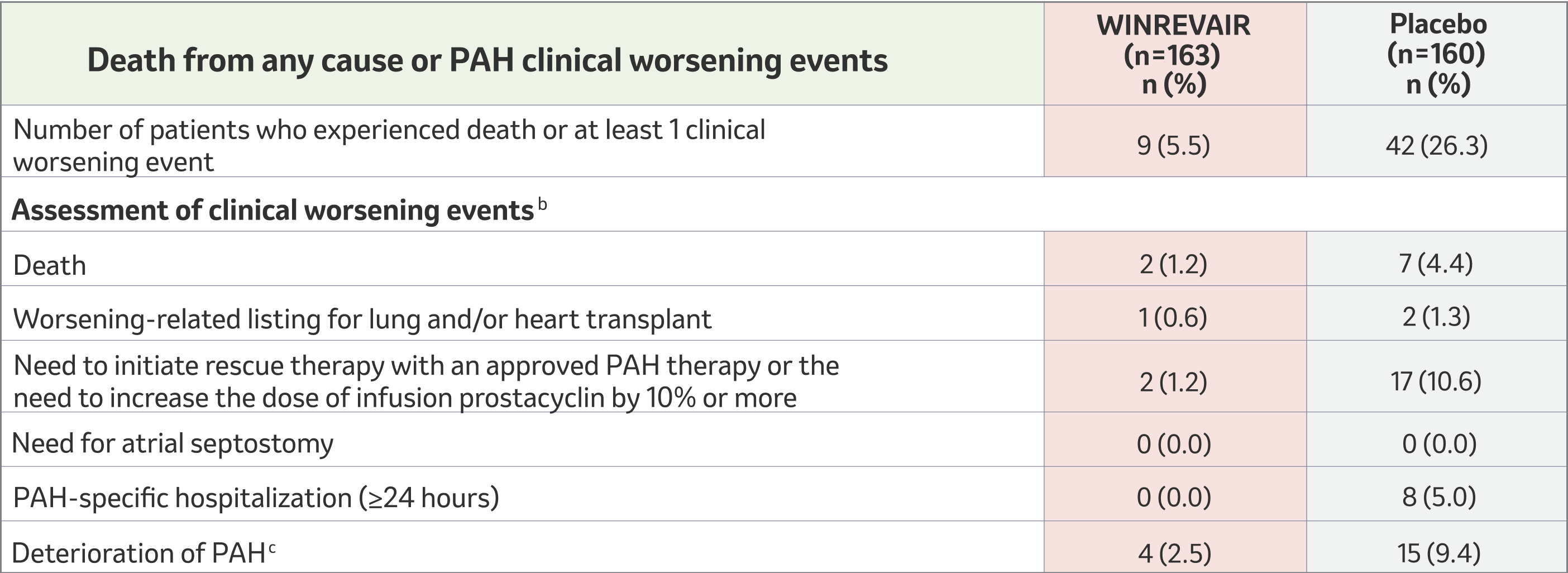
aThese outcomes were captured until the last patient completed the week 24 visit (median duration of exposure 33.6 weeks).
bA patient can have more than 1 assessment recorded for their clinical worsening.
cDeterioration of PAH is defined by both of the following events occurring at any time, even if they began at different times, as compared to their baseline values: worsened WHO FC (II to III, III to IV, II to IV, etc.) and decrease in 6MWD by ≥15% (confirmed by two 6-minute walk tests at least 4 hours apart but no more than 1 week).
Hemodynamics and Cardiac Function
A greater decrease from baseline was observed with WINREVAIR vs placebo in 2 key measures of hemodynamics and cardiac function
PVR

-235 dynes*sec/cm5
Median treatment difference at week 24 (95% CI: -288, -181)
(-2.9 Wood units)
NT-proBNP
-442 pg/mL
Median treatment difference at week 24 (95% CI: -574, -310)
CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance; NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide.
Reference:
1. Hoeper MM, Badesch DB, Ghofrani HA, et al; STELLAR Trial Investigators. Phase 3 trial of sotatercept for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(16):1478-1490.
Report exposure during pregnancy or lactation to the Merck Sharp & Dohme, LLC Adverse Event reporting line at 1-877-888-4231
