Sustained clinical response in adults
In the same studies, DIFICID demonstrated superior sustained response rate vs vancomycin through 25 days after end of treatment
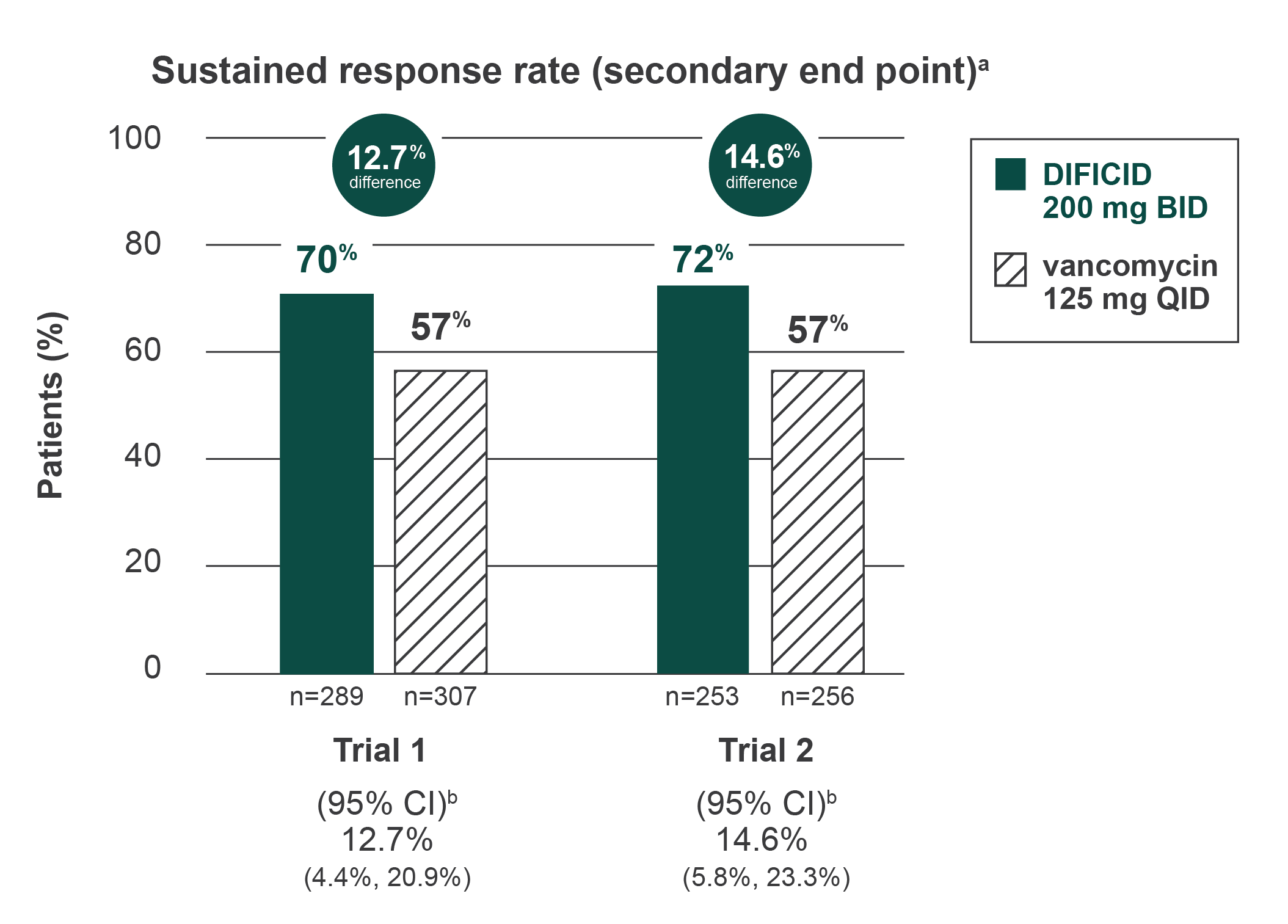
aSustained response was defined as clinical response at the end of treatment and survival without proven or suspected CDAD recurrence through 25 days beyond the end of treatment.
bCI was derived using Wilson’s score method. Approximately 5% to 9% of the data in each trial and treatment arm were missing sustained response information and were imputed using multiple imputation method.
Since clinical success at the end of treatment and mortality rates were similar across treatment arms (approximately 6% in each group), differences in sustained response were due to lower rates of proven or suspected CDAD during the follow-up period in DIFICID patients.
Efficacy in BI isolates: In patients infected with a BI isolate, similar rates of clinical response at the end of treatment and during the follow-up period were seen in fidaxomicin-treated and vancomycin-treated patients. However, DIFICID did not demonstrate superiority in sustained response when compared with vancomycin in these patients.
