Mechanism of action for ZERBAXA® (ceftolozane and tazobactam)
ZERBAXA combines a novel cephalosporin that has bactericidal action with a proven beta-lactamase inhibitor
Learn about:
Mechanism of action
Antimicrobial activity
ZERBAXA has been shown to be active against the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections.
Hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP)
Gram-negative bacteria
| Enterobacter cloacae | Escherichia coli |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Klebsiella oxytoca |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Proteus mirabilis |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Serratia marcescens |
Complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis (cUTIs)
Gram-negative bacteria
| Escherichia coli | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Proteus mirabilis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAIs) combined with metronidazole
Gram-negative bacteria
| Enterobacter cloacae | Escherichia coli |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Proteus mirabilis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Gram-positive bacteria
| Streptococcus anginosus |
| Streptococcus constellatus |
| Streptococcus salivarius |
Anaerobic bacteria
| Bacteroides fragilis |
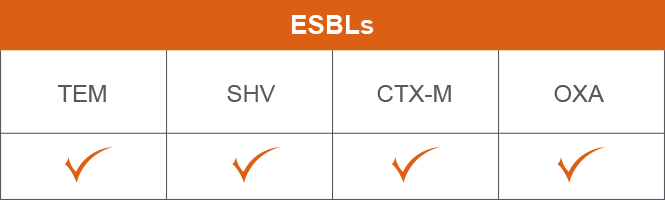
Mechanisms of resistance
ZERBAXA is active in vitro in the presence of select key mechanisms of resistance
P. aeruginosa isolates with the most prevalent mechanisms of resistance (AmpC, loss of outermembrane porin, upregulation of efflux pumps) and some ESBLs