Study results in HSCT
Learn about:
Prophylaxis through Week 14 (~100 days) post-HSCT
Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 24 (~168 days) in HSCT patients
PREVYMIS demonstrated significant efficacy vs placebo in the primary endpoint: Clinically significant CMV infectiona through Week 24 (NC=F approach)b
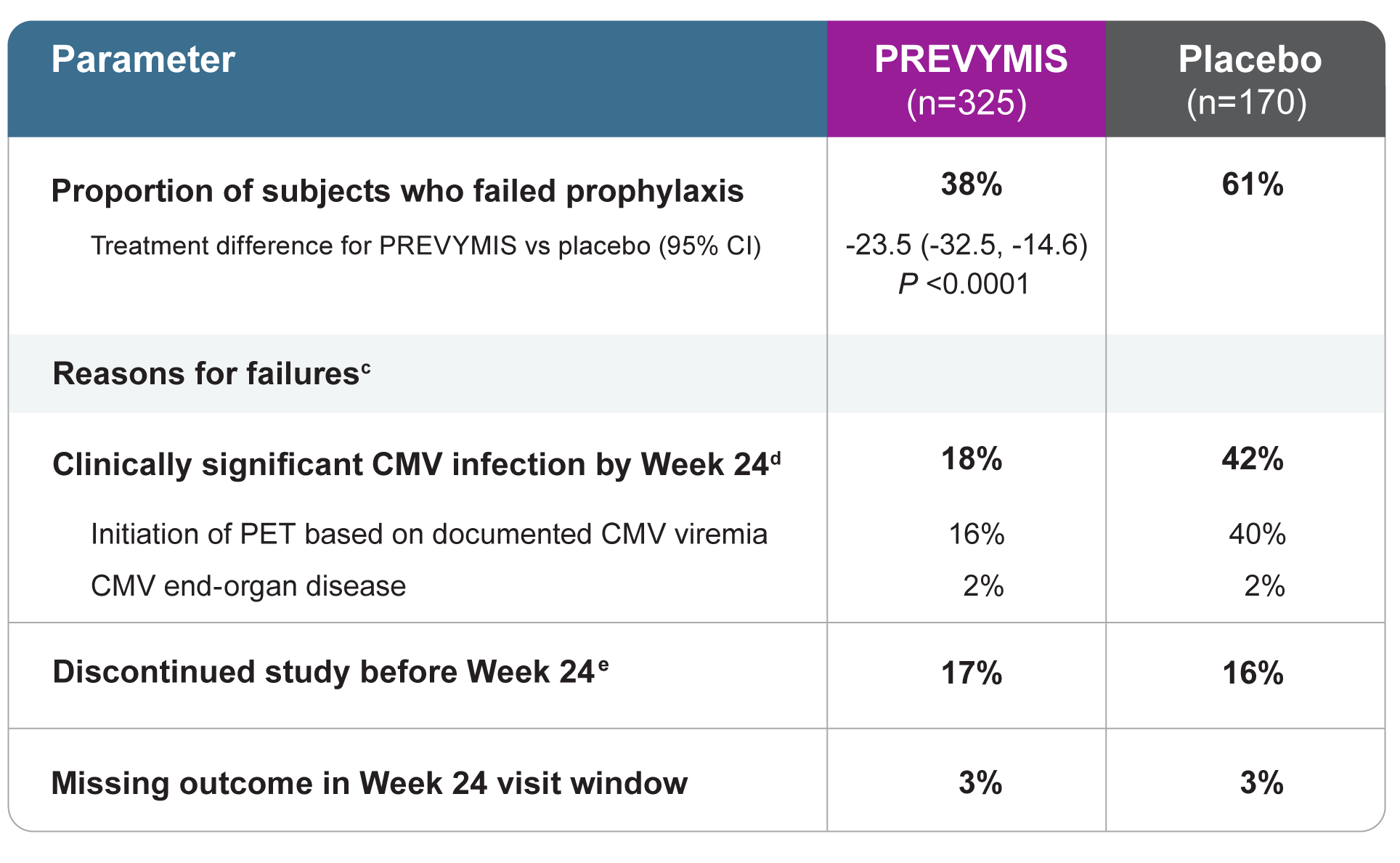
(a) Clinically significant CMV infection was defined as either the occurrence of CMV end-organ disease or initiation of anti-CMV PET, based on documented CMV viremia and the clinical condition of the patient. Viremia was determined using the Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan® assay; lower limit of quantification was 137 IU/mL, which is approximately 150 copies/mL.
(b) The Noncompleter=Failure (NC=F) approach was used in which patients who discontinued from the study prior to Week 24 post-HSCT or had a missing outcome at Week 24 post-HSCT were counted as failures.
(c) The categories of failure are mutually exclusive and based on the hierarchy of categories in the order listed.
(d) Through Week 14, 8% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and 39% of subjects in the placebo group experienced clinically significant CMV infection.
(e) Reasons for discontinuation included adverse event (AE), death, lost to follow-up, physician decision, and withdrawal by subject.
Rate of clinically significant CMV infection
Significantly lower rate of onset of clinically significant CMV infection for PREVYMIS vs placebo1
Factors associated with clinically significant CMV infection between Week 14 and Week 24 post-HSCT among PREVYMIS patients included:
- High-risk stratum for CMV reactivation at baseline
- Having GVHD
- Steroid use at any time after randomization
Mortality analysis in HSCT
Lower all-cause mortality for PREVYMIS vs placebo in HSCT patients2-4 a,b
(a) Data through week 24 post-HSCT P=0.04.
(b) Data through week 48 post-HSCT P=0.21, not significant.
High- and low-risk strata
Efficacy results were consistent across high- and low-risk strata for CMV reactivation.
Copyright © 2017 Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.4
Overview of CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] status and additional risk factors at baseline

Baseline data collected at randomization in the phase 3 trial.
The majority of patients in the phase 3 trial were R+ with no additional risk factors at baseline. Thirty percent of patients were R+ with ≥1 of the following additional risk factors and were placed in the high-risk stratum:
- Related donor with human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatch
- Haploidentical donor
- Unrelated donor with HLA mismatch
- Use of umbilical cord blood
- Use of ex vivo T-cell–depleted grafts
- GVHD requiring systemic corticosteroids
Prophylaxis from Week 14 (~100 days) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT
PREVYMIS demonstrated significant efficacy vs placebo
Primary endpoint: Clinically significant CMV infectiona through Week 28 post-HSCT (OF approachb)
Eligible subjects who completed PREVYMIS prophylaxis through ~100 days post-HSCT were randomized to receive PREVYMIS or placebo from Week 14 through Week 28 post-HSCT
Efficacy results in HSCT recipients at risk for late CMV infection and disease
(a) Clinically significant CMV infection (csCMVi) was defined as the occurrence of either CMV end-organ disease or initiation of anti-CMV PET based on documented CMV viremia and the clinical condition of the subject.
(b) The Observed Failure (OF) approach was used, where subjects who discontinued prematurely from the study without viremia or were missing data at the timepoint were not counted as failures. The number of subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 28 without viremia was 14 (9.7%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 0 in the placebo arm. The number of subjects with a missing outcome in the Week 28 visit window was 3 (2.1%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 4 (5.4%) in the placebo arm, none had prior viremia.
(c) The categories of failure are mutually exclusive and based on the hierarchy of categories in the order listed.
(d) Clinically significant CMV infection was defined as CMV end-organ disease (proven or probable) or initiation of PET based on documented CMV viremia and the clinical condition of the subject.
Among subjects in the PREVYMIS group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 1.6% at the end of prophylaxis (Week 28) to 15.6% at Week 38. In the placebo group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 17.6% at Week 28 to 19.0% at Week 38. There were no additional cases of clinically significant CMV infection in either group between Weeks 38 and 48.
Risk factors for late CMV infection and disease
At study entry, all subjects had risk factors for late CMV infection and disease, with 64% having two or more risk factors. The risk factors included:
- HLA-related (sibling) donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following three HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B, or -DR
- Haploidentical donor
- Unrelated donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following four HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1
- Use of umbilical cord blood as stem cell source
- Use of ex vivo T-cell-depleted grafts
- Receipt of anti-thymocyte globulin
- Receipt of alemtuzumab
- Use of systemic prednisone (or equivalent) at a dose of ≥1 mg/kg of body weight per day
References
- Marty FM, Ljungman P, Chemaly RF, et al. Letermovir prophylaxis for cytomegalovirus in hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(25):2433–2444. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1706640
- Ljungman P, Schmitt M, Marty FM, et al. A mortality analysis of letermovir prophylaxis for cytomegalovirus (CMV) in CMV seropositive recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1525-1533. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146004/bin/ciz490_suppl_supplementary_figure_1.pdf
- Ljungman P, Schmitt M, Marty FM, et al. A mortality analysis of letermovir prophylaxis for cytomegalovirus (CMV) in CMV seropositive recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1525-1533. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146004/bin/ciz490_suppl_supplementary_figure_2.pdf
- Ljungman P, Schmitt M, Marty FM, et al. A mortality analysis of letermovir prophylaxis for cytomegalovirus (CMV) in CMV seropositive recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1525-1533. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz490